Best pH Level for Drinking Water?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is recommended that the level of pH value of drinkable water should be between 6.5 to 8.5. Water below the range of 6.5 is considered acidic and may corrode metal pipes. It may also leach metals such as lead, copper, and zinc into the water. On the other hand, water with a pH above 8.5 can be alkaline and may have a bitter taste. The water above the range of 8.5 tends to deposit into pipes and fixtures.
It’s important to note that pH value of drinkable water is just one factor to consider when evaluating the safety of drinking water. Other factors like total dissolved solids (TDS), chlorine levels, and the presence of contaminants should also be checked before consuming water. We must drink safe water with a balanced pH level, TDS, and chlorine level away from impurities.
What Is Ph Level?
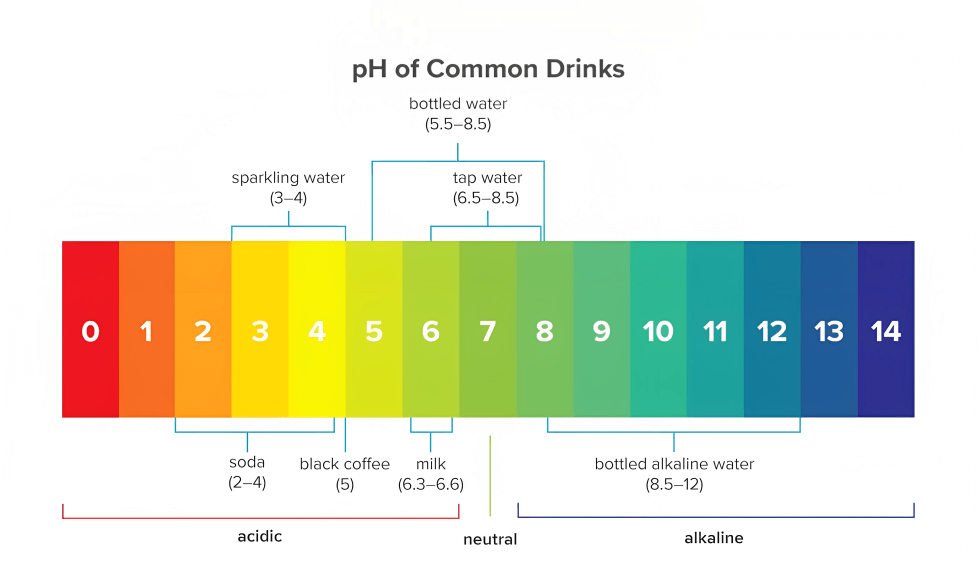
pH level measures the acidity or alkalinity of any solution, such as water, chemical solutions, etc. The term “pH” stands for “potential of hydrogen.” It measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. A pH value is expressed on a scale of 0-14, where a value of 7 is considered neutral. A pH value below 7 indicates that a solution is acidic, while a pH above 7 means that a solution is alkaline or basic. Each pH value below 7 is ten times more acidic than the next higher value, and each pH value above 7 is ten times less acidic than the next lower value.
For example, a pH of 5 is ten times more acidic than a pH of 6 and one hundred times (10 times 10) more acidic than a pH of 7. The pH of water is an essential factor in determining its quality and suitability for different uses, including drinking, agricultural, and industrial processes.
How Ph Level Affects the Water Suitable for Drinking?
The pH value of drinkable water can affect its suitability for drinking in a few ways:
Taste
The pH of water can affect its taste. Water that is too acidic or too alkaline may have a bitter or metallic taste, respectively. It can make the water unpleasant and unhealthy to drink.
Corrosion
Water with a too-low pH (acidic) can be corrosive to metal pipes and fixtures. It can cause metals like lead and copper to leach into the water. These metals, especially when they are in high concentration, can be harmful to human health.
Disinfection
Water with a too high pH (alkaline) can affect chlorine and other disinfectants used to treat the water. It can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria and other microorganisms in the water, making it unsafe to drink.
Mineral solubility
The solubility of minerals in water can be affected by their pH level. Water that is too acidic can dissolve metals like lead and copper, while water that is too alkaline can cause minerals like calcium and magnesium to precipitate out of the water and form deposits.
Therefore, it is essential to maintain a pH level between 6.5 and 8.5 in drinking water to ensure it is safe and suitable for human consumption.
How to Test the Ph Level of Water
There are several methods for testing the pH value of drinkable water, including:
pH test strips
pH test strips are small pieces of paper or plastic that change color when dipped into the water. These strips come with a color chart that can be used to match the color of the strip according to the pH value.
Digital pH meters
Digital pH meters are electronic devices that measure the pH level of water and display the value on a screen. These meters can be more accurate than pH test strips but more expensive than other tests.
Chemical titration tests
Chemical titration tests involve adding a chemical agent to a water sample and slowly adding another reagent until the solution changes color. The amount of reagent needed to change the color can be used to determine the pH level of the water.
It’s important to note that different testing methods may have different levels of accuracy, and it’s essential to follow the instructions carefully for each technique. Additionally, it’s crucial to use testing equipment designed for the specific pH range of the tested water. If you’re not comfortable testing the pH level of your drinking water yourself, you can contact a professional testing service to do it for you.
How to Adjust the Ph of Water
There are several ways to adjust the pH level of water, including:
Adding alkaline substances
If the pH level of water is too low (acidic), adding an alkaline substance like baking soda, calcium carbonate, or lime can help to raise the pH level. The amount of alkaline substance needed will depend on the volume of water being treated and the degree of acidity.
Adding acidic substances
If the pH level of water is too high (alkaline), adding an acidic substance like vinegar, citric acid, or sulfuric acid can help to lower the pH level. Again, the amount of acidic substance needed will depend on the volume of water being treated and the degree of alkalinity.
Using a neutralizer
A pH neutralizer can be added to water to bring the pH level closer to neutral (pH 7). A neutralizer is typically made up of a blend of alkaline and acidic compounds and is designed to stabilize the pH level of water.
It’s important to note that adjusting the pH level of water can be a delicate process. m oreover, if done incorrectly, it may have unwanted repercussions. Therefore, its crucial to follow instructions carefully and to test the water frequently to ensure the desired pH level is maintained.
Health Effects: Consuming Water with a Ph Level Outside the Safe Range
Consuming water with a pH level outside the safe range can have adverse health effects. If the pH level is too low (acidic) it can cause several problems, including:
Dental erosion
Acidic water can erode tooth enamel, leading to tooth decay and other dental problems.
Gastrointestinal problems
Drinking water with a low pH level can cause gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Skin irritation
Acidic water can irritate the skin and cause rashes, itching, and other skin problems.
If the pH level is too high (alkaline), it can causefollowing health problems-
Alkalosis
Consuming water with a high pH level can lead to alkalosis. It is a condition where the body’s pH level becomes too alkaline. This can cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and muscle twitching.
Bone density loss
Drinking water with a high pH level can lead to loss of bone density. It increases the risk of osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions.
Skin irritation
Alkaline water can also irritate the skin and cause dryness, itching, and other skin problems.
Please note that the effects of consuming water with an incorrect pH level can vary depending on the individual and the degree of deviation from the safe range.
Natural Variations
Natural variations in the pH level of water can occur due to different factors, including the source of the water, geological conditions, and weather patterns.
For example, groundwater sources may have a naturally low pH level due to the presence of minerals like iron or sulphur. On the other hand, surface water sources may have a higher pH level due to the presence of organic matter.
In some cases, natural variations in the pH level of water may fall outside of the safe range for drinking water. In these cases, water treatment may be necessary to adjust the pH level to a safe level for consumption.
However, in many cases, natural variations in pH may be harmless or even beneficial. For example, some people believe that drinking alkaline water can help to neutralize the Racid in the body and improve overall health.
There is limited scientific evidence to support the health benefits of alkaline water, and it may not be appropriate for everyone. It’s also essential to maintain a safe pH level for drinking water to ensure optimal health and well-being. If you’re concerned about the pH level of your drinking water, you can contact a professional water testing service to have it tested and to determine if any treatment is necessary.







